CS 210: Mathematical Logic Notes
Preliminaries(预备知识)
set集合
intension:内涵
The intension of a set is its description or defining properties, i.e., what is true about members of a set. (对概念的定义)extension:外延
The extension of a set is its members or contents. (概念所代表的对象)$\mathbb{P}$= Prime numbers 质数
外延原理:
The two sets A and B are equal (A = B) if and only if A and B have the same members.
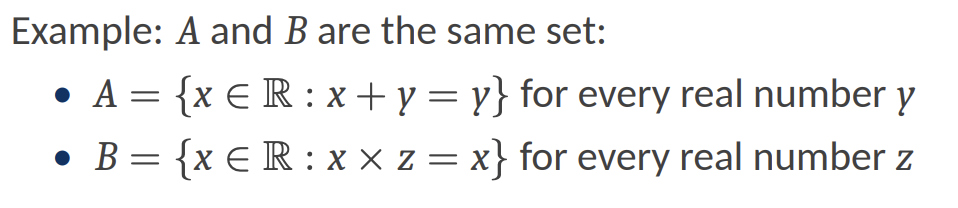
- 集合中可以重复,且无序。
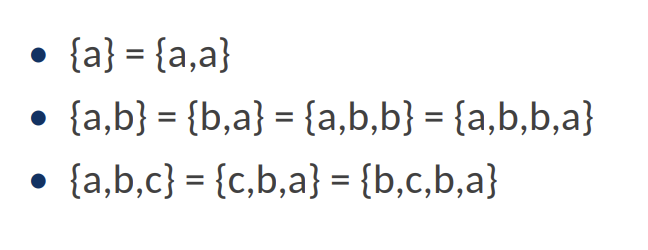
- subset:子集
Proper subset 真子集
Power set 幂集:含有该集合的所有子集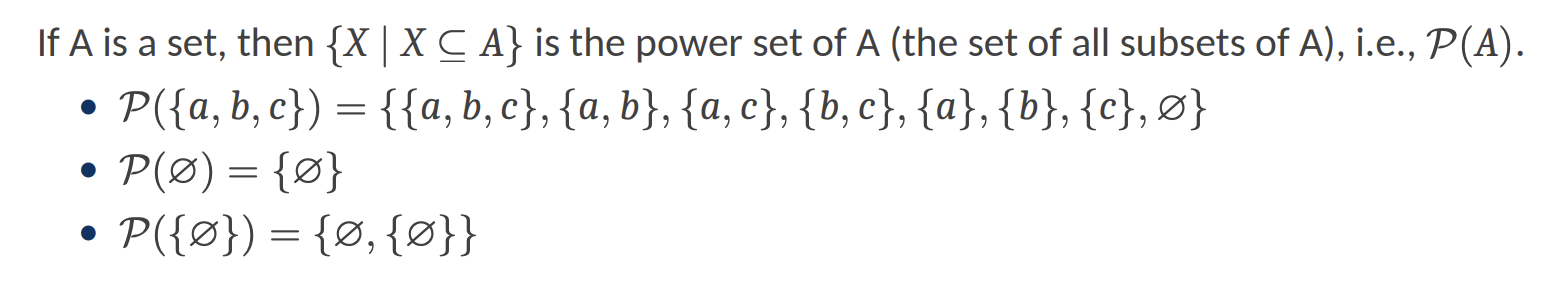
- set operations

- n-tuples:有序n元组
在数理中,tuple 是一个有限元素且有序的数组集合- tuple may contain multiple instances of the same element, (1,2,2,3)$\ne$(1,2,3)
- tuple elements are ordered
- tuple has a finite number of elements while a set may not
- Binary Relation二元关系
- Intuitively, a binary relation from a set X to a set Y is a set of ordered pairs where x is an element of X and y is an element of Y.
- $A \times B$ denotes the Cartesian product (笛卡尔积) of set A and B: : {⟨x, y⟩ | x ∈ A and y ∈ B} (the set of all ordered pairs where x is in A and y is in B.)
- The statement $⟨x, y⟩ ∈ R$ reads ”x is R-related to y”, and is denoted by $R(x, y)$ or $xRy$.

- n-ary relation多元关系
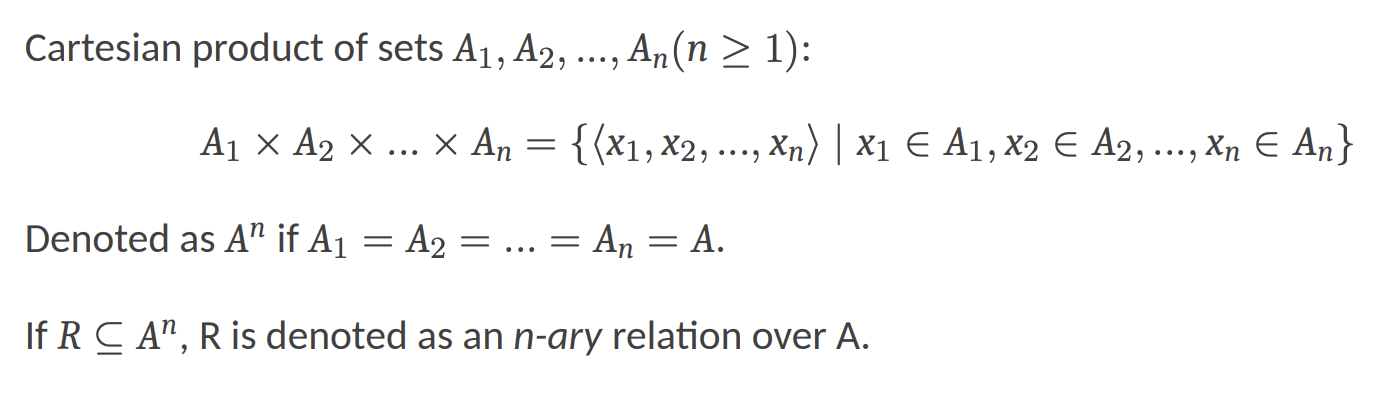
Equivalence Relation
- Equivalence Relation等价关系
- 如果R是一个等价关系,R要满足三个性质:reflexive(自反)、symmetric(对称)、transitive(传递)。

- 比如说“=”关系就是最基本的等价关系

- 如果R是一个等价关系,R要满足三个性质:reflexive(自反)、symmetric(对称)、transitive(传递)。
- Equivalence Relation等价类
- 对于集合A上的等价关系R,元素x的等价类为$$
[x]{R} { \gamma \in A | xRy }$$$[x]{R}$ 是集合A中所有等价于x的元素 - Theorem: If R is an equivalence relation over A, then every a ∈ A belongs to exactly one equivalence class.
如果R是集合A上的一个等价类,那么集合中的每一个元素都属于一个类 - Theorem: Given an equivalence relation on set A, the collection of equivalence classes forms a partition (划分) of set A.
等价类可以将集合A进行划分
- 对于集合A上的等价关系R,元素x的等价类为$$
Partial Order relation
Partial Order relation偏序关系
- 偏序关系满足三个性质
- reflexive 自反
- 自反性质的举例 “=”、”≥”、”≤”是自反的,“>”是不自反的
- antisymmetric 反对称的
- for all x, y ∈ A,if xRy and yRx, then x=y.
- transitive 传递

- reflexive 自反
- 一个有意思的例子
- The binary relation ”x is divisible by y” on the set of positive integers is a partial order. It has no minimal elements, and 1 is a maximal element.
这很好的说明偏序关系中的“大小关系”与“数值大小”无关 - 对于上面这个例子,可以联系化学中的“广度量 extensive properties”和“强度量 intensive properties”的概念,偏序关系是一种强度量
- The binary relation ”x is divisible by y” on the set of positive integers is a partial order. It has no minimal elements, and 1 is a maximal element.
Total Order relation
Total Order Relation全序关系
- 全序关系(Total Order Relation),也称为全序或线性序,是数学中的一个概念,用于描述集合中元素之间是否可以完全排序,即对于任意两个元素,我们总是可以确定一个元素是大于还是小于另一个元素。
定义
一个二元关系 R定义在集合 A 上,如果满足以下三个条件,则称 R 是一个全序关系:
- 自反性(Reflexivity):对于所有 $a \in A$,有 $a R a$ 。
- 反对称性(Antisymmetry):对于所有 $a, b \in A$ ,如果 $a R b$ 且 $b R a$ ,则 $a = b$ 。
- 可比性(Totality)或连通性(Connectivity):对于所有 $a \in A$,要么 $a R b$ ,要么 $b R a$ ,或者两者都成立。
例子
- 自然数上的小于或等于关系:自然数集上的小于或等于关系是一个全序关系,因为自然数可以完全排序。
- 实数上的小于关系:实数集 $\mathbb{R}$ 上的小于关系 也是一个全序关系,因为任意两个实数都可以比较大小。
- 字符串字典序:字符串集合上的字典序(或词序)是一个全序关系,因为可以确定任意两个字符串谁在谁之前。
与偏序关系的比较
全序关系是偏序关系(Partial Order Relation)的一种特殊情况。偏序关系同样要求自反性和反对称性,但只需要满足以下条件:
- 可比性:对于所有 $a, b \in A$ ,要么 $a R b$ ,要么 $b R a$ ,但不一定两者都必须成立。
这意味着在偏序关系中,可能存在一些元素对 a 和 b 既不是 a R b 也不是 b R a ,这在全序关系中是不可能的。
小于不是偏序关系,也不是全序关系,是严格偏序关系
Functions
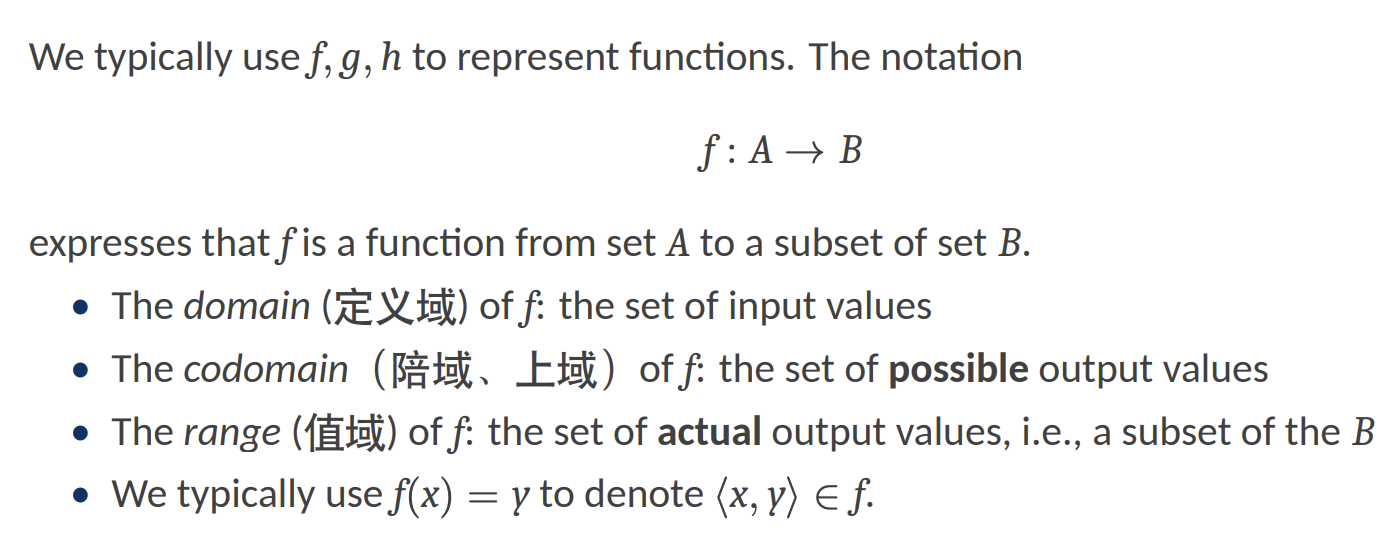
- domain 定义域
- codomain 陪域,上域
- range 值域

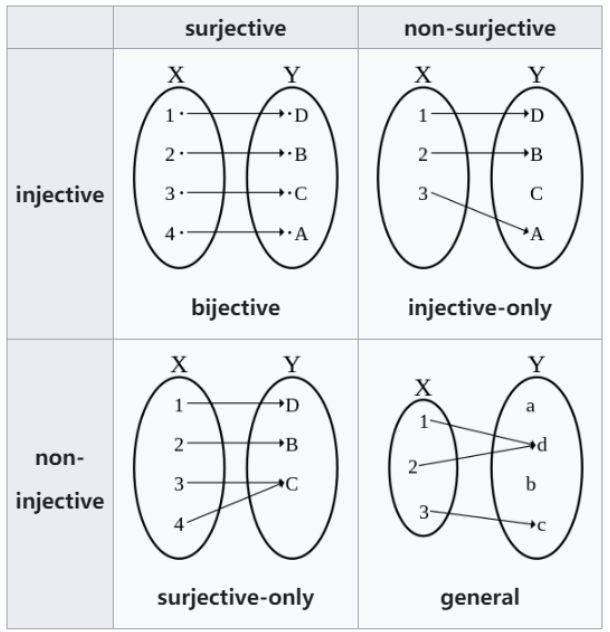
- injective:单射或一一映射
- Surjective:满射
- bijective:双射
rigorously:严格地
4 Mathematical Definitions & Proof
- Inductive Definition (归纳定义)
- 归纳定义通常包含两个主要部分:
- 基础情况(Base Case):定义中的一个声明,指定了集合中至少存在一个或一组特定的元素。
- 归纳步骤(Inductive Step):定义中的一个声明,说明了如何通过已经定义的元素来生成新的元素。
- Proof by Induction (归纳证明)
- Recursive Definition (递归定义)
- Proof Contradiction (反证法)



